Understanding the 4 types of sentences in English is an essential step for learners who want to master grammar and communication. Sentences are the building blocks of language, and each type carries a unique purpose in expressing ideas. By learning how declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences work, students gain confidence in both writing and speaking. This blog post explains their definition, structure, and examples in a clear and simple way, making English easier to understand for learners at any level.
Table of Contents
What Sentences are in English with Example?
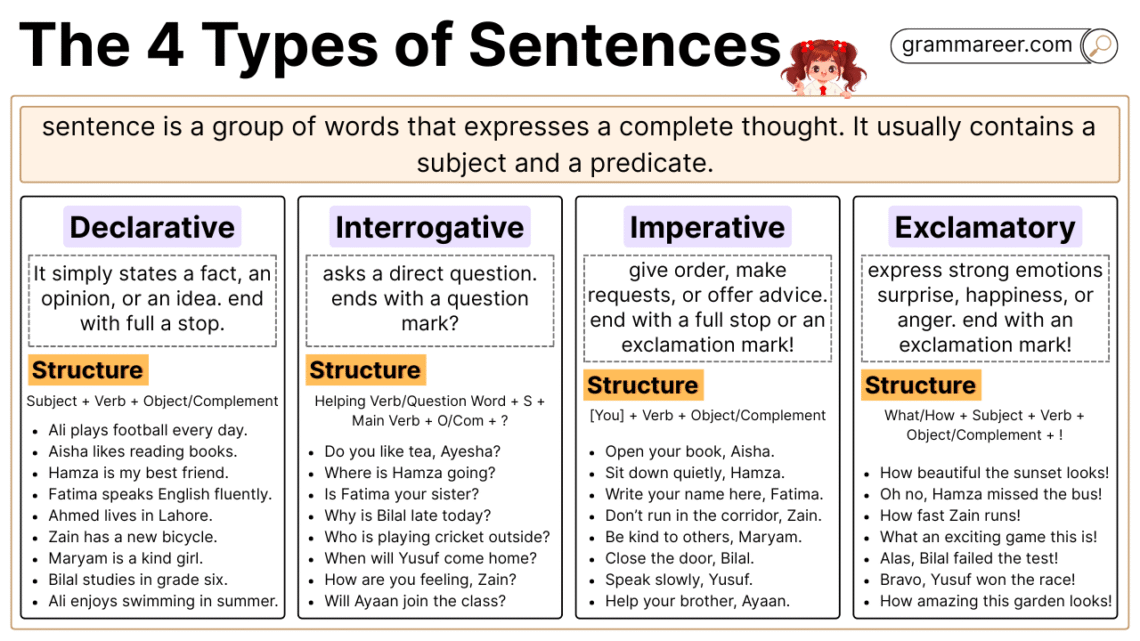
In English grammar, a sentence is a group of words that expresses a complete thought. It usually contains a subject and a predicate. A subject tells who or what the sentence is about, while a predicate describes the action or state of being.
- Aisha reads a book.
In this sentence, “Aisha” is the subject and “reads a book” is the predicate. Together, they form a complete idea, which makes it a sentence.
4 Types of Sentences in English
English sentences can be divided into four main types. Each serves a different purpose in communication:
| Type of Sentence | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Declarative | To state information | Fatima is learning English. |
| Interrogative | To ask a question | Are you going to school, Ahmed? |
| Imperative | To give a command or request | Please open the window, Ayaan. |
| Exclamatory | To show strong feelings | What a beautiful garden this is! |
Declarative Sentences and Example
A declarative sentence is the most common type in English. It simply states a fact, an opinion, or an idea. These sentences always end with a full stop.
- Maryam studies in the library.
The first sentence is correct because it states information and ends with a full stop. The second is incorrect because the question mark changes its purpose.
Declarative Sentence Structure
The structure of a declarative sentence usually follows:
Subject + Verb + Object/Complement
- Bilal plays football in the park.
Here, “Bilal” is the subject, “plays” is the verb, and “football in the park” is the object with detail.
Interrogative Sentences and Example
An interrogative sentence asks a direct question. It always ends with a question mark and often begins with a helping verb or question word such as what, where, when, why, who, or how.
- Where is Hamza going?
The first is correct because it uses the proper question format and ends with a question mark. The second is incorrect because it lacks correct order and punctuation.
Interrogative Sentence Structure
The structure usually follows:
Helping Verb/Question Word + Subject + Main Verb + Object/Complement + ?
- Is Zain writing a letter?
In this example, “Is” is the helping verb, “Zain” is the subject, and “writing a letter” is the main action.
Imperative Sentences and Example
Imperative sentences are used to give orders, make requests, or offer advice. The subject is often “you,” but it is usually not written in the sentence. These sentences may end with a full stop or an exclamation mark, depending on the tone.
- Please help your brother, Yusuf.
The first sentence is correct because it gives a polite request without an unnecessary subject. The second is incorrect because it repeats the subject awkwardly.
Imperative Sentence Structure
The structure usually follows:
[You] + Verb + Object/Complement
- Close the door, Fatima.
Here, the hidden subject is “you,” and the command is “close the door.”
Exclamatory Sentences and Example
Exclamatory sentences express strong emotions such as surprise, happiness, or anger. They always end with an exclamation mark.
- How wonderful this meal tastes!
The first is correct because it shows excitement and ends with an exclamation mark. The second is not exclamatory, though it is grammatically correct, because it lacks emotion.
Exclamatory Sentence Structure
The structure often follows:
What/How + Subject + Verb + Object/Complement + !
- What a nice gift Ali received!
Here, “What a nice gift” expresses emotion, “Ali” is the subject, and “received” is the action.
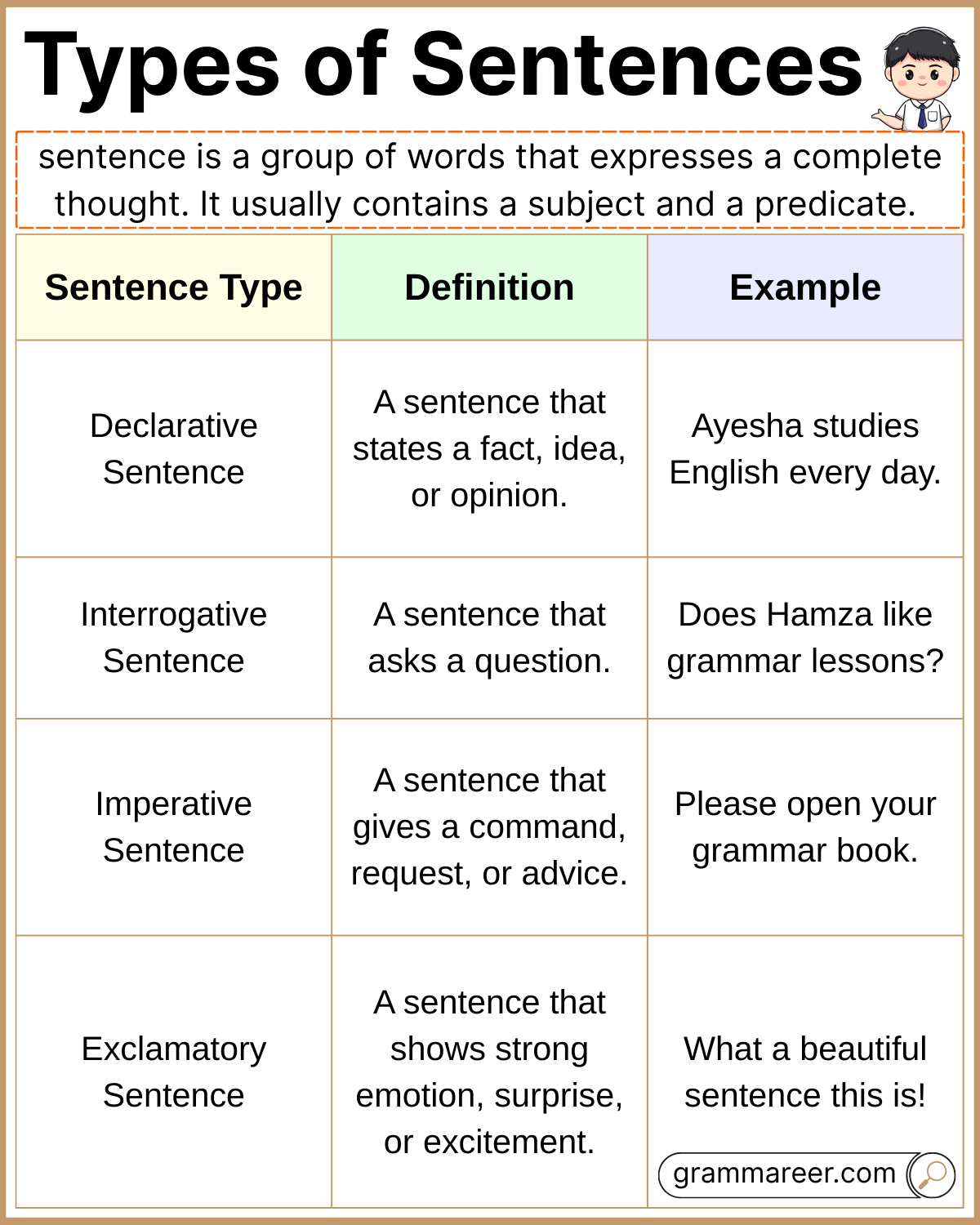
Sentences Chart (Types, Rules, and Examples)
| Sentence Type | Definition | Key Rule / Structure | Example Sentence |
|---|---|---|---|
| Declarative Sentence | A sentence that states a fact, idea, or opinion. | Subject + Verb (+ Object). Ends with a period (.) | Ayesha studies English every day. |
| Interrogative Sentence | A sentence that asks a question. | Begins with a Wh-word (what, why, how, etc.) or auxiliary verb (is, do, can, etc.). Ends with a question mark (?) | Does Hamza like grammar lessons? |
| Imperative Sentence | A sentence that gives a command, request, or advice. | Starts with the base verb. Subject is usually “you” (understood). Ends with a period (.) or exclamation mark (!) | Please open your grammar book. |
| Exclamatory Sentence | A sentence that shows strong emotion, surprise, or excitement. | Can begin with What or How. Ends with an exclamation mark (!) | What a beautiful sentence this is! |
FAQs about 4 Types of Sentences
The four types are declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory. Each type serves a special purpose: stating facts, asking questions, giving commands, or showing emotions.
Look for sentences that state information and end with a period. Example: “Sara loves her new dress.” It is declarative because it tells something directly without asking or commanding.
We use interrogative sentences to ask for details, clarify information, or gather knowledge. Example: “When is your exam, Omar?” The question form helps seek an answer.
Yes, it can. Adding words like please makes the command softer. Example: “Please pass the pen, Aisha.” The word please makes the request more respectful.
Strong feelings and an exclamation mark make a sentence exclamatory. Example: “What a bright day it is!” The tone and punctuation show emotion.
You May Also Like