Is it tricky for you to figure out how main verbs and helping verbs work in sentences?
You’re not alone! Many English learners often get confused by verbs like is, have, and will when they appear before another verb. These are called helping verbs, also known as auxiliary verbs. They work with the main verb to show tense, mood, or voice. These verbs are not used independently because they always come with a main verb to complete the meaning of the sentence.
In this article, you’ll find clear examples and everything you need to remember when using helping verbs.
Ans: Helping verbs add support to the main verb and they tell when or how something happens.
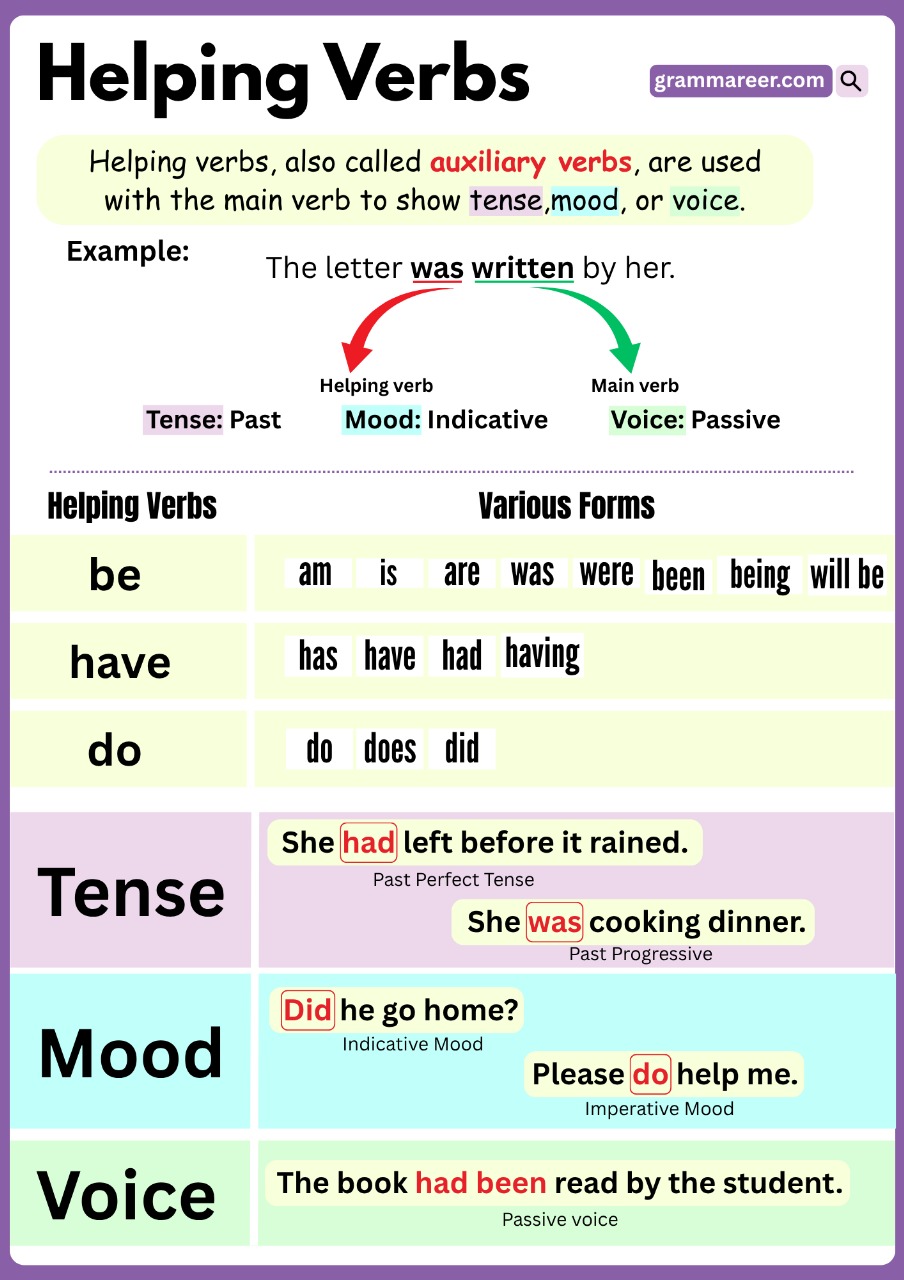
Table of Contents
What is a Helping Verb?
A helping verb is a word that comes before the main verb to help show when something happens or what the action means. It cannot be used alone. They must always come with a main verb to make the sentence complete. A helping verb, just like its name, helps the main verb and is used to show changes in tense, mood, or voice in a sentence.
Types of Helping Verbs
There are two types of helping verbs: primary helping verbs and modal helping verbs.
Primary Auxiliary Verbs:
Primary helping verbs such as be, have, and do are used with main verbs to build verb tenses, questions, negative sentences, and passive voice structures.
An explanation of each primary auxiliary verb is given below.
1.”Be“:
- We use “be” to make continuous tenses and passive sentences.
- Examples:
- Continuous Tenses:
- He is watching a movie. (present continuous)
- We were walking home when it started to rain. (past continuous)
- Passive Voice:
- The letter was delivered this morning. (past simple passive)
- Dinner is being served now. (present continuous passive)
- Continuous Tenses:
2. “Have”:
- Have helps show that an action is completed, either in the past, present, or future — that’s what we call perfect tenses.
- Examples:
- I have eaten breakfast. (Present Perfect)
- She had left before the meeting started. (Past Perfect)
- They will have finished the work by next week. (Future Perfect)
3. “Do”:
- We use do and did to ask questions or say something in a negative way, especially in the present and past simple tenses.
- Examples:
- Do you like ice cream?
- Did they go to the party?
- I don’t understand the instructions.
- They didn’t finish their homework.
Modal Auxiliary Verbs:
Modal verbs are words like can, should, and must that help us talk about things like possibility, intention, ability, or need.
There are 9 common modal verbs in English, such as follow:
- Can, could
- Shall, should
- Will, would
- May, might
- Must, ought to
Examples:
- I might go to the party if I finish work early. (possibility)
- You should drink more water during the day. (advice)
- He can lift that heavy box by himself. (ability)
- We must wear seatbelts while driving. (necessity)
- She would help if she had more time. (willingness)
Why do we use helping verbs?
Auxiliary verbs are used to avoid repeating the main verb after a conjunction. Instead, we just use an auxiliary verb like do, is, or have after “but” to keep it short and smooth.
Examples: Auxiliary verbs to avoid repetition
- I’m not going to the party, but Sara is.
- He enjoys cooking, but his brothers don’t.
Common Helping Verb List with Example Sentences
The following table provides examples of common helping verbs and how they function within sentences:
| Helping Verb | Example Sentence |
|---|---|
| is | Fatima is reading a book. |
| are | They are playing football. |
| was | He was watching TV. |
| were | They were preparing dinner. |
| has | Ahmed has completed his homework. |
| have | We have seen the movie. |
| had | She had visited the museum before. |
| can | Maria can solve the puzzle. |
| could | He could climb the hill easily. |
| will | He will travel to Lahore tomorrow. |
| shall | I shall call you later. |
| may | She may attend the meeting. |
| might | They might arrive late. |
| must | You must follow the rules. |
Fatima is performing the ongoing action of reading. Similarly, “are” indicates an ongoing activity, “was” and “were” refer to past continuous actions. “Has” and “have” show completed actions, while “can,” “could,” “will,” and others express abilities, future actions, or possibilities.
Helping Verb vs. Main Verb
Main verbs and helping verbs do different jobs in a sentence. The main verb tells us what is really happening. It shows the main action like eat, run, go, sleep, or work. Without the main verb, we won’t know what the subject is doing.
The helping verb doesn’t show action by itself. It just helps the main verb. It tells us when something is happening (like now, in the past, or in the future), or helps make negative sentences and questions.
Examples:
- She sings beautifully.
- sings is the main verb – it tells what she does.
- She is singing a song.
- “is” is the helping verb – it helps the main verb.
- singing is the main verb – it shows the action.
Helping Verb vs. Linking Verb – What’s the Difference?
Both helping verbs and linking verbs may look the same sometimes (like is, am, are, was, were), but they play very different role in a sentence. While helping verbs assist the main verb, linking verbs connect the subject to additional information about the subject.
Example of Helping Verbs:
- He is happy.
- “is” is a linking verb – it links the subject He to the word happy (which tells us more about him).
Example of Linking Verbs:
- He is running.
- “is” is a helping verb – it helps the main verb running and shows the action is happening right now.
List of Helping Verbs of All Tenses
The table below lists helping verbs categorized by tenses:
| Tense | Examples | Helping Verbs |
| Present | He is working. | is, am, are |
| Past | She was singing. | was, were |
| Future | They will arrive soon. | will, shall |
| Present Perfect | He has finished the task. | has, have |
| Past Perfect | They had gone home. | had |
| Future Perfect | We will have completed it. | will have, shall have |
FAQs
Helping verbs, or auxiliary verbs, are verbs that assist the main verb in forming tenses, moods, voices, or questions. Examples include “is,” “have,” and “will.”
Helping verbs support the main verb by adding grammatical meaning, such as tense or mood. Main verbs express the primary action or state.
Yes, a sentence can include multiple helping verbs. For example, “He will have been working for hours.”
Am, Is, Are, Was, Were, Be, Being, Been, Has, Have, Had, Do, Does, Did, Can, Could, Shall, Should, Will, Would, May, Might, Must, Ought to, Need to, Dare to, Used to
Final Thoughts
As we learned, helping verbs may be small, but they play a big role in making our sentences clear, complete, and grammatically correct. They help form questions, negatives, and different tenses — all the things that make English sound natural and smooth.
Understanding how helping verbs work can really improve your grammar and make your writing and speaking more confident. So whether you’re learning English or just brushing up, knowing these little helpers is a smart step forward.
You May Also Like