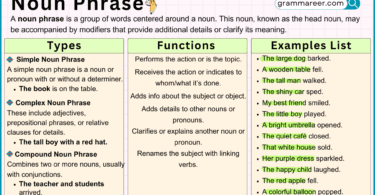
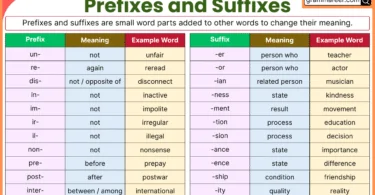
Parts of speech are important in learning English because they help us understand how words work together in sentences. Just like puzzle pieces fit together to create a picture, parts of speech fit together to create meaningful sentences. When we know the different parts of speech, we can use them to build sentences correctly. It’s like having a set of rules or guidelines that show us how words should be used. For example, nouns are like the names of people, places, or things, while verbs show actions or states of being. By knowing the parts of speech, we can express ourselves clearly and accurately. We can choose the right words to describe things, show actions, or express ideas. It’s like having a toolbox of words that we can use to communicate effectively.
Table of Contents
8 Parts of Speech
- Noun
- Pronoun
- Adjective
- Verb
- Adverb
- Preposition
- Conjunction
- Interjection
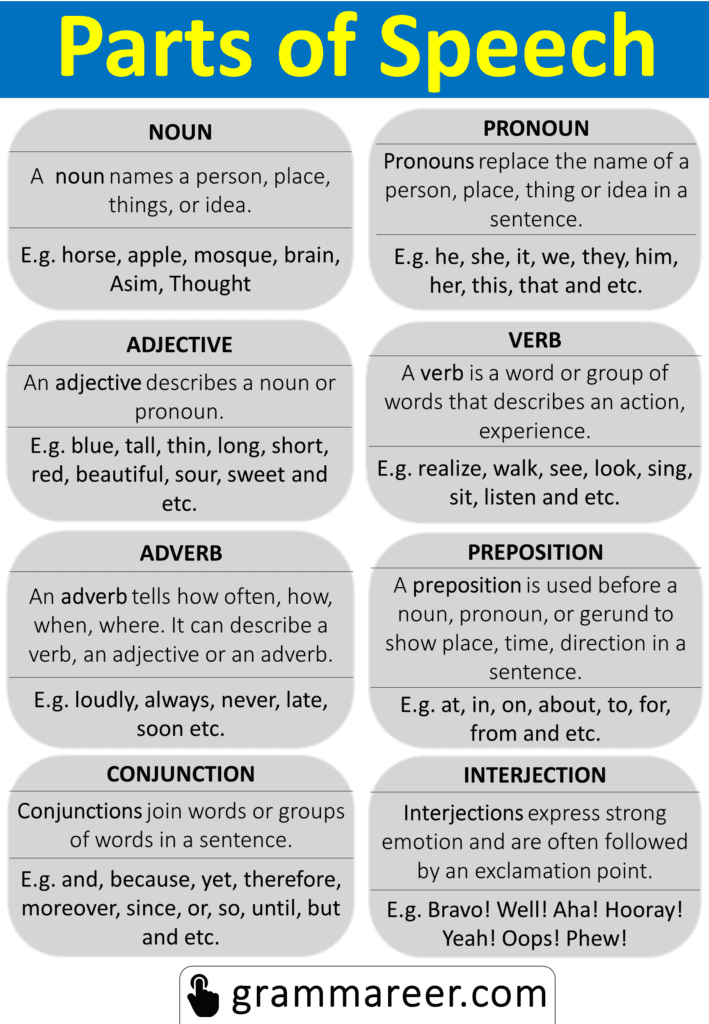
All Parts of Speech Chart with Examples
Noun
A noun is a word that gives a name to a person, place, thing, or idea. It helps us identify and talk about the stuff around us.
- People: teacher, doctor, student, friend, mother, father
- Places: city, park, school, restaurant, beach, home
- Things: book, table, chair, car, phone, computer
Types of Nouns
- Common Nouns:
- Person: man, teacher, friend
- Place: city, park, school
- Thing: book, table, car
- Proper Nouns:
- Person: John, Mary, Michael
- Place: Paris, London, New York
- Thing: Coca-Cola, Nike, Titanic
- Concrete Nouns:
- Dog, tree, house, ball, flower
- Abstract Nouns:
- Love, happiness, courage, friendship, knowledge
- Collective Nouns:
- Team, family, flock, herd, swarm
- Countable Nouns:
- Cat (singular), cats (plural)
- Book (singular), books (plural)
- Chair (singular), chairs (plural)
- Uncountable Nouns:
- Water, happiness, information, sugar, knowledge
Pronoun
A pronoun is a word that is used in place of a noun. It helps us avoid repeating the same noun over and over again in a sentence. Instead, we can use a pronoun to refer to the noun.
- I, you, he, she, it, we, they
Types of Pronouns
- Personal Pronouns:
- I, you, he, she, it, we, they
- Possessive Pronouns:
- Mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs
- Demonstrative Pronouns:
- This, that, these, those
- Reflexive Pronouns:
- Myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, themselves
- Interrogative Pronouns:
- Who, whom, whose, which, what
- Relative Pronouns:
- Who, whom, whose, which, that
- Indefinite Pronouns:
- Someone, anyone, nobody, everybody, something, anything, nothing, everything
- Reciprocal Pronouns:
- Each other, one another
Adjective
An adjective is a word that describes or modifies a noun or pronoun. It provides more information about the qualities, characteristics, or attributes of the noun or pronoun it is describing.
- Beautiful, Few, These, Her, Which
Types of Adjectives
- Descriptive Adjectives:
- Big: a big house
- Red: a red car
- Beautiful: a beautiful sunset
- Quantitative Adjectives:
- Many: many books
- Few: a few friends
- Several: several cups
- Demonstrative Adjectives:
- This: this book
- That: that pen
- These: these shoes
- Those: those flowers
- Possessive Adjectives:
- My: my dog
- Your: your house
- His: his car
- Her: her cat
- Our: our team
- Interrogative Adjectives:
- Which: which color
- What: what time
- Whose: whose bag
- Comparative Adjectives:
- Taller: a taller building
- More interesting: a more interesting movie
- Bigger: a bigger house
- Superlative Adjectives:
- Tallest: the tallest tree
- Most delicious: the most delicious cake
- Happiest: the happiest child
- Proper Adjectives:
- American: American culture
- Italian: Italian cuisine
- French: French fashion
Verb
A verb is a word that expresses an action, occurrence, or state of being. It describes what someone or something does, experiences, or is.
- Feel, seem, taste, run, eat, jump, think, write, dance
Types of verbs
Here are the types of verbs explained in easy language:
- Action Verbs:
- Run, eat, jump, think, write, dance
- Linking Verbs:
- Be, appear, become, feel, seem, taste
- Helping Verbs:
- Can, will, must, should, have, may
- Modal Verbs:
- Could, would, should, might, must
- Transitive Verbs:
- Eat (I eat an apple.), read (She reads a book.), kick (He kicks the ball.)
- Intransitive Verbs:
- Sleep, laugh, run, arrive
- Regular Verbs:
- Talk (present), talked (past), talked (past participle)
- Irregular Verbs:
- Go (present), went (past), gone (past participle)
Adverb
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb. It provides more information about how, when, where, why, or to what extent an action occurs or a quality is expressed.
- Always, often, Carefully, soon, never
All Types of Adverbs
- Adverbs of Time:
- Yesterday, today, now, soon, always
- Adverbs of Place:
- Here, there, inside, outside, nearby
- Adverbs of Manner:
- Carefully, quickly, happily, softly, loudly
- Adverbs of Degree:
- Very, extremely, quite, too, completely
- Adverbs of Frequency:
- Always, often, sometimes, rarely, never
- Adverbs of Reason:
- Therefore, because, hence, thus, consequently
- Adverbs of Purpose:
- To, in order to, so as to, for
- Interrogative Adverbs:
- How, when, where, why, how often
- Relative Adverbs:
- When, where, why
- Conjunctive Adverbs:
- However, therefore, furthermore, meanwhile, nevertheless
Preposition
A preposition is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and another word in a sentence. It indicates location, time, direction, manner, or other relationships.
- At, Before, From, Towards, By, For
Types of Prepositions
- Prepositions of Place:
- In: She is in the room.
- On: The book is on the table.
- At: They met at the park.
- Under: The cat is under the bed.
- Above: The bird is flying above the trees.
- Prepositions of Time:
- Before: We had dinner before the movie.
- After: She arrived after the party started.
- During: I read a book during my vacation.
- At: They will meet at 7 p.m.
- On: The concert is on Friday.
- Prepositions of Direction:
- To: He walked to the store.
- From: She received a letter from her friend.
- Into: The children jumped into the pool.
- Out of: The cat jumped out of the box.
- Towards: He ran towards the finish line.
- Prepositions of Manner:
- With: She painted the picture with a brush.
- By: The book was written by the author.
- Like: He sings like a professional.
- In: She spoke in a soft voice.
- Prepositions of Cause:
- Because of: The game was canceled because of the rain.
- Due to: The flight was delayed due to bad weather.
- For: He received applause for his performance.
- Thanks to: Thanks to her help, I finished the project.
- Prepositions of Possession:
- Of: The pages of the book are torn.
- With: She entered the room with a smile.
- Prepositions of Agency:
- By: The song was written by John.
- With: The vase was made with clay.
- Prepositions of Condition:
- In: She is in good health.
- On: The dog is lying on the mat.
- Prepositions of Purpose:
- For: She bought flowers for her mother.
- To: They went to the beach for relaxation.
- Compound Prepositions:
- According to: According to the report, the sales increased.
- In front of: The car is parked in front of the house.
- Next to: The bookstore is next to the café.
Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that connects words, phrases, or clauses together in a sentence. It helps to show relationships between these elements and coordinate their meaning within a sentence.
- But, Although, Whether…or, However, Where
Types of Conjunctions
- Coordinating Conjunctions:
- And: I like apples and oranges.
- But: He studied hard, but he failed the exam.
- Or: Would you like tea or coffee?
- So: She studied well, so she passed the test.
- Yet: He was tired, yet he continued to work.
- Subordinating Conjunctions:
- Because: He stayed home because he was sick.
- Although: Although it was raining, they went for a walk.
- If: If you study hard, you will succeed.
- While: She read a book while waiting for the bus.
- Correlative Conjunctions:
- Either…or: You can either have pizza or pasta.
- Neither…nor: Neither he nor she attended the party.
- Both…and: She is both intelligent and hardworking.
- Whether…or: I haven’t decided whether to go or stay.
- Conjunctive Adverbs:
- However: She studied hard; however, she didn’t perform well.
- Therefore: It rained heavily; therefore, the match was canceled.
- Meanwhile: He cooked dinner; meanwhile, she set the table.
- Subordinating Conjunctions (Time/Place):
- Before: She left before I arrived.
- Where: I found a book where I least expected.
Interjection
An interjection is a word or phrase that expresses strong emotions, sudden reactions, or exclamations. It is used to convey feelings or add emphasis to a sentence.
- Ouch!, Hooray!, Bravo!, Fantastic!, Oh no!
Types of Interjections
- Exclamatory Interjections:
- Wow! That’s an amazing view!
- Oh no! I forgot my keys!
- Ouch! That hurt!
- Yay! We won the game!
- Greeting Interjections:
- Hi! How are you doing?
- Hello! Nice to meet you.
- Hey! What’s up?
- Joyful Interjections:
- Hooray! We’re going on vacation!
- Yippee! It’s my birthday!
- Yahoo! I aced the exam!
- Surprise Interjections:
- Whoa! That’s incredible!
- Oh my goodness! I can’t believe it!
- Good heavens! Look at the size of that!
- Approval Interjections:
- Bravo! Well done!
- Excellent! You did a great job!
- Fantastic! I love your idea!
- Disapproval Interjections:
- Ugh! I can’t believe this mess.
- Oh no! That’s not good.
- Yuck! This food tastes awful.
Read More