A noun is a word that is used to name a person, place, thing, or idea. It’s a word that helps us identify and talk about people, objects, locations, or concepts. Nouns are one of the fundamental parts of speech and play a crucial role in constructing sentences. There are several types of Nouns based on their characteristics. Proper nouns are specific names of people, places, or things, and they are always capitalized. For example, “John” is a proper noun that refers to a specific person. Common nouns, on the other hand, are general names for people, places, or things, and they are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence. For instance, “cat” is a common noun that can refer to any cat in general.
Examples of nouns:
- Person: John, Mary, teacher, doctor
- Place: New York, beach, school, park
- Thing: car, book, table, dog
- Idea: love, freedom, courage, happiness
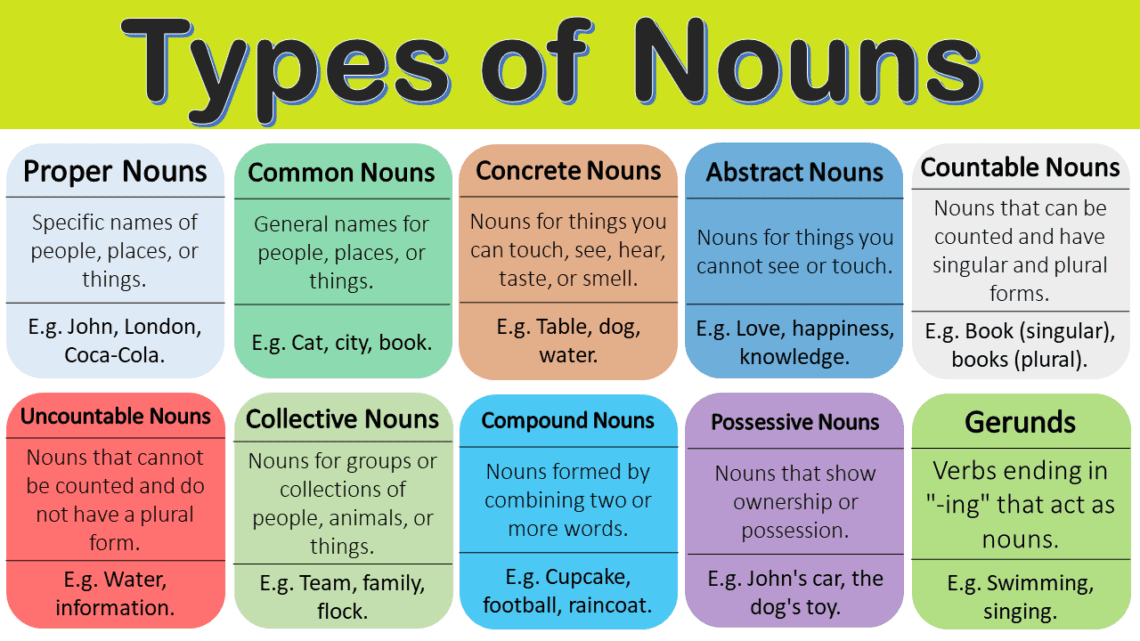
Types of Nouns Chart
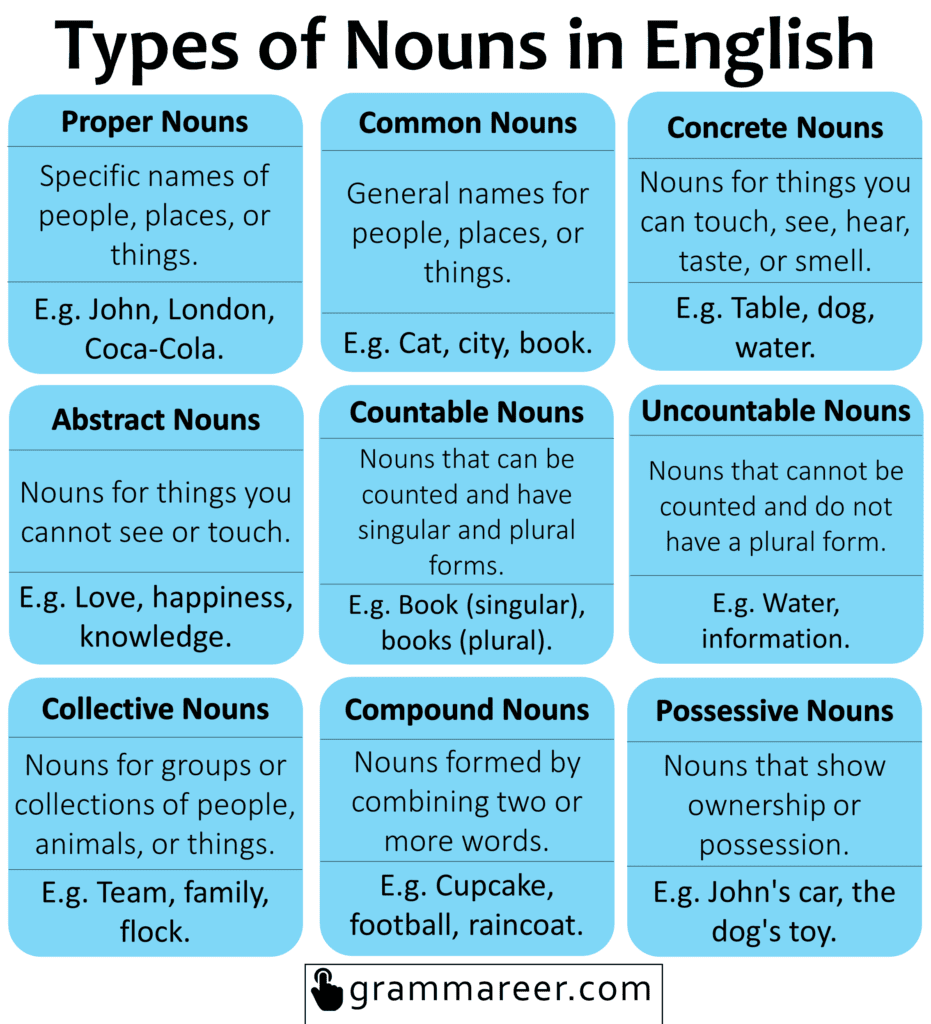
| Types | Definitions | Examples |
| 1. Proper Nouns | Specific names of people, places, or things. They always start with a capital letter. | John, London, Coca-Cola. |
| 2. Common Nouns | General names for people, places, or things. They refer to ordinary objects. | Cat, city, book. |
| 3. Concrete Nouns | Nouns for things you can touch, see, hear, taste, or smell. They represent physical objects. | Table, dog, water. |
| 4. Abstract Nouns | Nouns for things you cannot see or touch. They represent ideas, emotions, or qualities. | Love, happiness, knowledge. |
| 5. Countable Nouns | Nouns that can be counted and have singular and plural forms. | Book (singular), books (plural). |
| 6. Uncountable Nouns | Nouns that cannot be counted and do not have a plural form. | Water, information. |
| 7. Collective Nouns | Nouns for groups or collections of people, animals, or things. | Team, family, flock. |
| 8. Compound Nouns | Nouns formed by combining two or more words. | Cupcake, football, raincoat. |
| 9. Possessive Nouns | Nouns that show ownership or possession. They have an apostrophe and an “s” (‘s) at the end. | John’s car, the dog’s toy. |
| 10. Gerunds | Verbs ending in “-ing” that act as nouns. They can be subjects or objects in a sentence. | Swimming, singing. |
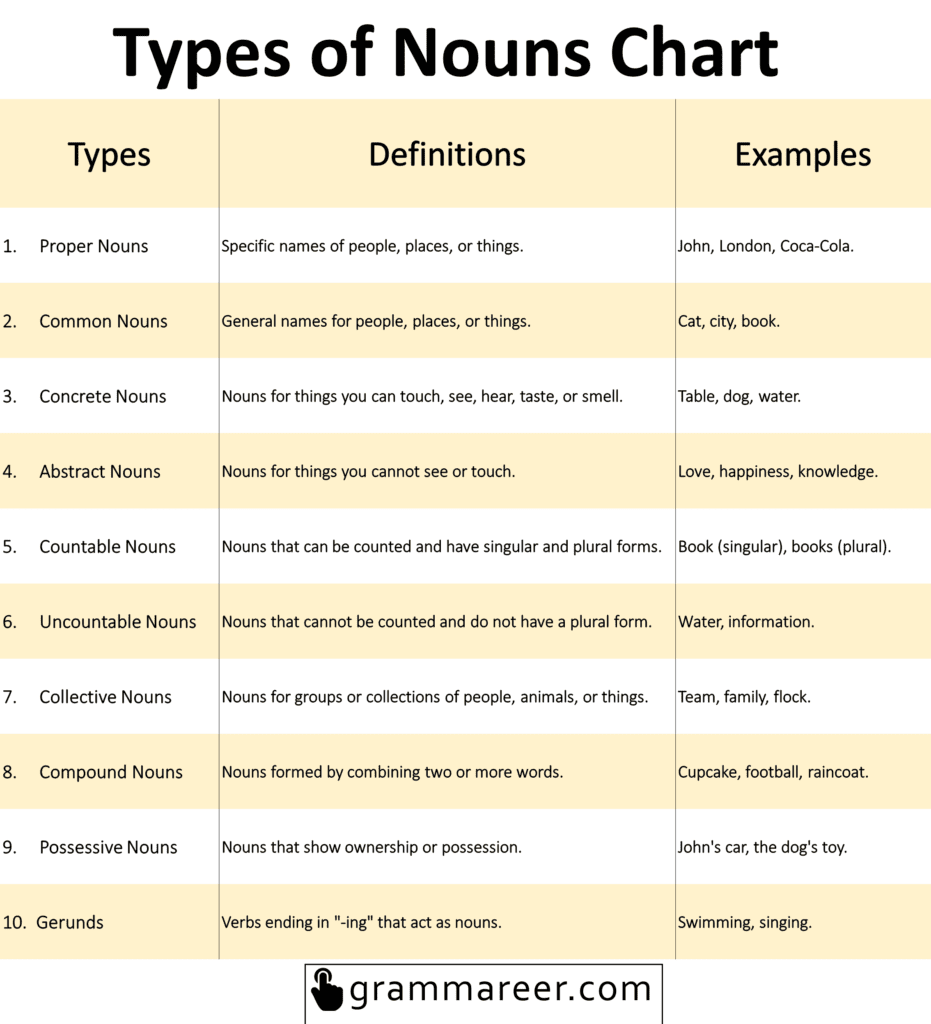
Types of Nouns Chart
Types of Nouns
- Proper Nouns: A proper noun is a specific name given to a particular person, place, organization, or thing. It is used to distinguish and identify a unique entity. Proper nouns are always capitalized, regardless of their position in a sentence. Here are some examples:
- Person: John, Mary, David Beckham
- Place: London, Paris, Grand Canyon
- Organization: Google, Apple, United Nations
- Event: Olympic Games, Super Bowl, Christmas
- Book: Pride and Prejudice, Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets
- Common Nouns: Common nouns are general names for people, places, things, or ideas. Unlike proper nouns, they do not refer to specific individuals, locations, or entities. Common nouns are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence. Here are some examples:
- Person: teacher, doctor, student
- Place: city, park, school
- Thing: table, book, dog
- Idea: love, freedom, happiness
- Concrete Nouns: Concrete nouns are a type of noun that refer to physical objects or substances that can be perceived through the senses. These nouns represent things that have a tangible existence and can be seen, touched, heard, smelled, or tasted. Here are some examples of concrete nouns:
- Objects: chair, car, phone, computer
- Animals: dog, cat, elephant, bird
- Fruits: apple, banana, orange, strawberry
- Elements: water, fire, air, earth
- Abstract Nouns: Abstract nouns are a type of noun that refer to ideas, concepts, qualities, or states that cannot be perceived through the senses. Unlike concrete nouns, which represent physical objects, abstract nouns represent intangible things that exist in the realm of thoughts, feelings, and emotions. Here are some examples of abstract nouns:
- Love
- Courage
- Honesty
- Freedom
- Joy
- Knowledge
- Justice
- Beauty
- Patience
- Wisdom
Abstract nouns represent concepts or qualities that cannot be seen, heard, smelled, tasted, or touched, but they hold significant meaning in our lives and help us express emotions, beliefs, and values. They are often the building blocks of expressing deeper thoughts and ideas in language.
- Countable Nouns: Countable nouns are a type of noun that can be counted and have both singular and plural forms. These nouns refer to objects or entities that can be quantified or enumerated. Countable nouns can be used with a specific number or quantity, and they can also be made plural by adding an “-s” or “-es” to the end of the word. Here are some examples of countable nouns:
- Singular: book, chair, apple, dog Plural: books, chairs, apples, dogs
- Singular: car, house, pen, student Plural: cars, houses, pens, students
- Singular: tree, flower, bird, river Plural: trees, flowers, birds, rivers
Countable nouns can be easily counted and expressed in specific numbers. They can be modified by quantifiers such as “a,” “an,” “many,” “few,” or numerical expressions like “two,” “three,” “several,” etc.
- Uncountable Nouns: Uncountable nouns, also known as non-count nouns or mass nouns, are a type of noun that cannot be counted as discrete individual units. These nouns typically represent substances, concepts, or qualities that are perceived as a whole or as uncountable entities. Uncountable nouns do not have a plural form and are not used with numbers or the indefinite article “a” or “an.” Here are some examples of uncountable nouns:
- Water
- Information
- Happiness
- Music
- Knowledge
- Advice
- Money
- Time
- Furniture
- Love
Uncountable nouns refer to abstract or non-physical concepts, substances, or qualities that cannot be easily divided or quantified into separate units. They are often used to express broader ideas or collective concepts.
- Collective Nouns: Collective nouns are a type of noun that represents a group or collection of people, animals, or things. They are singular in form but refer to multiple individuals or objects as a single entity. Collective nouns are used to describe a group acting as one unit. Here are some examples of collective nouns:
- Team (a team of players)
- Family (a family of four)
- Herd (a herd of cattle)
- Flock (a flock of birds)
- Swarm (a swarm of bees)
- Compound Nouns: Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a new word with a distinct meaning. These words are joined together, either with or without hyphens, to form a single noun. Compound nouns can be made up of different combinations, such as noun + noun, adjective + noun, verb + noun, or preposition + noun. Here are some examples of compound nouns:
- Noun + Noun:
- Cupcake (cup + cake)
- Football (foot + ball)
- Raincoat (rain + coat)
- Adjective + Noun:
- Blueberry (blue + berry)
- Blackboard (black + board)
- Coldwater (cold + water)
- Verb + Noun:
- Breakdown (break + down)
- Makeover (make + over)
- Takeoff (take + off)
- Preposition + Noun:
- Upstairs (up + stairs)
- Offspring (off + spring)
- Outfit (out + fit)
Compound nouns allow for more specific and concise descriptions by combining multiple words into a single noun. The meaning of a compound noun is often not directly deducible from the individual words used to form it.
- Noun + Noun:
- Possessive Nouns: Possessive nouns are nouns that indicate ownership, possession, or a relationship of belonging. They are formed by adding an apostrophe and an “s” (‘s) to the end of a noun, or just an apostrophe after a plural noun that already ends in “s.” Here are some examples of possessive nouns:
- Singular Nouns:
- John’s car
- The cat’s toy
- The company’s logo
- Plural Nouns:
- The students’ books
- The dogs’ leashes
- The houses’ roofs
- Plural Nouns Ending in “s”:
- The teachers’ lounge
- The countries’ capitals
- The cars’ colors
Possessive nouns show that something belongs to or is associated with a particular noun. They are used to indicate possession, attribution, or a relationship of ownership. By adding the appropriate apostrophe and “s” or just an apostrophe, possessive nouns help clarify the relationship between objects, people, or concepts in a sentence.
- Singular Nouns:
- Gerunds: A gerund is a verb form that functions as a noun in a sentence. It is created by adding the suffix “-ing” to the base form of a verb. Gerunds can be used as subjects, objects, or complements in sentences. Here are some examples of gerunds:
- Swimming is my favorite sport. (Subject)
- I enjoy singing in the shower. (Object)
- Her hobby is dancing. (Complement)
- Running can be a great form of exercise. (Subject)
- They discussed the importance of recycling. (Object)
- My passion is writing. (Complement)
Gerunds act as nouns, taking on roles that nouns typically fulfill in a sentence. They can be the subject of a sentence, the object of a verb or preposition, or serve as a complement. Gerunds allow us to discuss actions or activities as concepts or things rather than as verbs.
8 Types of Nouns with Examples