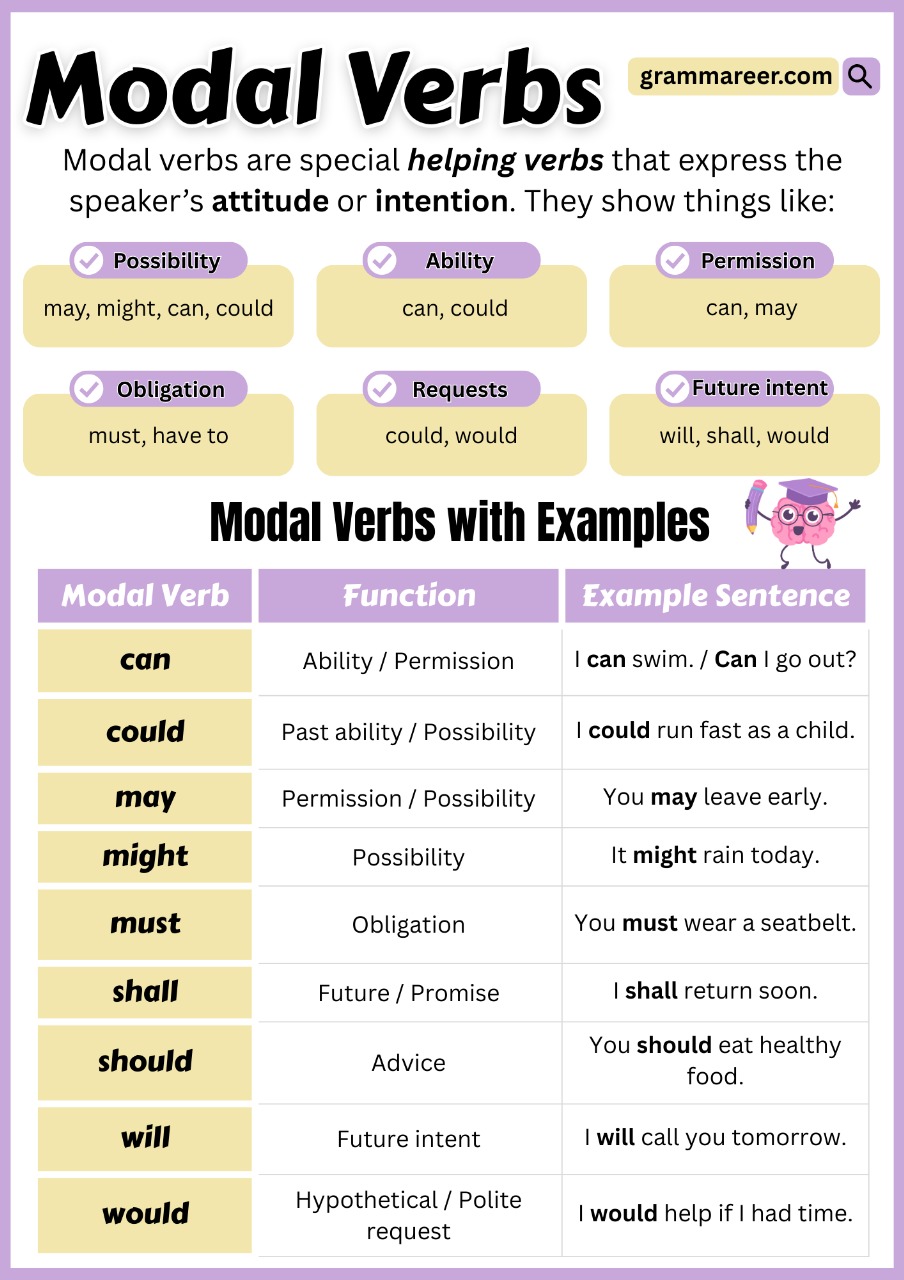
Have you ever wondered how we express ability, possibility, or permission in English? That’s where modal verbs come in. A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that works with the main verb to show what we can do, must do, or might happen. Words like can, could, may, might, must, and should help us express these ideas clearly and naturally.
In this article, you will learn what modal verbs are, how to use them, and see some simple examples to make your English stronger and more natural.
Table of Contents
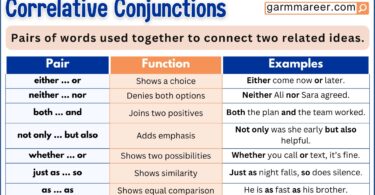
What Is a Modal Verb?
A modal verb (also called a helping verb) is used alongside with a main verb used to express possibility, ability, permission, or necessity. For example, in the sentence “You should eat your vegetables,” the modal verb “should” shows advice—it tells the person what is a good idea to do.
And in “I will visit my friend tomorrow,” the modal verb “will” shows the future—it tells us what is going to happen.
Examples:
- I can cook biryani.
- You should drink chai in the morning.
- He might come to the cricket match.
- You may take the rickshaw home.
Why Are Modal Verbs Used?
Modal verbs are used to express why something happens, what is possible, allowed, or necessary. Using them is easy! The basic structure is:
[modal verb] + [base verb]
Modal verbs never change. They don’t have past forms or infinitives.
For example:
| Verb Type | Example | Conjugation | Participle Forms | Infinitive Form |
| Normal Verb | eat | I eat. / He eats. (changes with subject) | eating (present participle) ate (past participle) | to eat |
| Modal Verb | can | I can. / He can. (never changes) | None | None |
Modal Verbs for Possibility
[can, could, may, or might + base verb]Examples:
- It can get very hot in Karachi during summer.
- (can shows something is possible)
- He could be at the market right now.
- (could shows a possible situation)
- You may see your friend at the park.
- (may shows a chance that it can happen)
- It might rain later today.
- (might shows a small possibility)
Modal Verbs for Ability
[can, could + base verb]
Examples:
- I can cook biryani.
- (can shows ability to do something)
- She can ride a bike very well.
- (can shows skill or ability)
- He could run very fast when he was younger.
- (could shows past ability)
- They could solve the problem with some help.
- (could shows possible ability in the past)
Modal Verbs for Permission
[can, could, may + base verb]Examples:
- You can take a rickshaw home.
- (can shows permission)
- Students may leave the classroom early today.
- (may shows formal permission)
- Could I borrow your pen?
- (could is a polite way to ask for permission)
Modal Verbs for Obligation
[must, have to, should + base verb]
Examples:
- You must wear a helmet while riding a bike.
- (must shows something is necessary)
- Students have to submit their assignments on time.
- (have to shows an obligation)
- We should respect our elders.
- (should shows advice or moral obligation)
Modal Verbs for Condition
[would, could, might + base verb]
Examples:
- I would help you if I had time.
- (would shows a possible action depending on a condition)
- She could win the match if she practices more.
- (could shows a possible result based on a condition)
- You might feel better if you drink some water.
- (might shows a possible outcome depending on a condition)
Another Way to Use Modal Verbs
You can also use modal verbs like this:
[modal verb] + have + [past participle]
This is used when talking about possibilities, abilities, permissions, obligations, or conditions that happened in the past. For example, it shows what could, might, or should have happened.
Modal Verbs and Auxiliary Verbs
Modal verbs are actually a type of auxiliary (helping) verb. Auxiliary verbs are used with a main verb to show tense, mood, or voice. But unlike modal verbs, regular auxiliary verbs change with the subject and must be conjugated.
Examples of auxiliary verbs in a sentence:
- Ali is making a cup of tea.
- Sara has finished her homework.
- Do you know the answer?
Modal verbs can also be used with auxiliary verbs to talk about past, continuous, or future actions. When a modal verb is followed by an auxiliary verb like have or be, the main verb uses either the past participle (like “eaten,” “gone,” or “written”) or the present participle (ending in “-ing”).
Examples of modal verbs combined with auxiliary verbs:
- She should have called me earlier.
- He might be sleeping right now.
- By 6 PM, Ali will have finished his project.
List of Modal Verbs
Here is a full list of all modal verbs:
- Can
- Could
- May
- Might
- Will
- Would
- Shall
- Should
- Must
- Ought to
- Have to
- Had better
How to use modal verb? (with examples)
In English grammar, as we learned modal verbs are helping verbs that do not change form based on the subject or tense. Unlike main verbs, modals are followed by the base form of another verb. They also do not take an “-s” ending for the third person.
✅ Example: She can drive to the store.
❌ Incorrect: She cans drive to the store.
Modal Verbs in Questions
Modal verbs are commonly used to ask questions, make requests, or ask about possibilities.
- Can I help you with anything?
- Would you like some coffee, Zain?
- May I ask you something?
Using modal verbs in questions makes your tone more polite and friendly. This is helpful in both formal and informal situations.
Modal Verbs in Negations
Modal verbs can also be used in negative sentences to indicate that something is not allowed, possible, or advisable. To make a negation, just add “not” after the modal verb.
- He cannot (can’t) attend the event tomorrow.
- You should not (shouldn’t) eat too much junk food, Imran.
- They might not be able to join us today.
Modal Verbs in Reported Speech
When using modal verbs in reported speech, some modals change while others remain the same.
- Direct Speech: “I will call you tomorrow,” Fatima said.
- Reported Speech: Fatima said that she would call me the next day.
Some modals like must and should remain unchanged, while can changes to could, and will changes to would when reported.
Examples of Modal Verbs in Sentences
- Can:
- Maryam can bake delicious cakes.
- Hamza can help you with your homework.
- Could:
- Usman could jump very high when he was younger.
- Sara could come if she finishes her tasks early.
- May:
- May I sit here, Zainab?
- It may snow tonight.
- Might:
- They might visit us this weekend.
- Hassan might be at the library now.
- Will:
- Fatima will join us for dinner.
- Will you attend the meeting, Bilal?
- Would:
- She would bring flowers every time she visited.
- I would love a glass of water, please.
- Shall:
- We shall overcome all difficulties.
- Shall we start the presentation?
- Should:
- You should exercise every day, Ali.
- Hina should apologize to her friend.
- Must:
- You must arrive on time, Aisha.
- They must follow the teacher’s instructions.
- Ought to:
- You ought to be kind to others.
- Ahmed ought to study for his exams.
- Have to:
- Sana has to leave early to catch the bus.
- Umar has to clean his room today.
- Had better:
- You had better submit your report soon.
- Fatima had better be careful with her words.
Why Modal Verbs Are Important?
The term “modal verb” comes from “modality,” which includes things like possibility, ability, and obligation. If you’re learning or teaching English, spending time on modal verbs is definitely worth it because they are essential for clear communication.
You might be surprised just how common modal verbs are. If you check Google’s Ngram viewer, you’ll see that words like “would” and “could” appear even more often than very common words like “see” and “work.” That shows how important they are in everyday English!
So yes, modal verbs really matter. Many language instructors even suggest that learning them should be one of the very first things for English learners.
FAQs
Modal verbs are helping verbs that work with main verbs to show ability, possibility, probability, or to emphasize necessity. They help make your sentences clearer and more meaningful.
Some common modal verbs in English are: will, would, can, could, may, might, shall, should, must, ought to.
Here are some examples of modal verbs in action:
• I can fix your computer if you want.
• You should drink water after exercising.
• He might join us for dinner tonight.
• Everyone must wear a helmet while riding a bike.
• Shall we go to the park this evening?
Final Thoughts
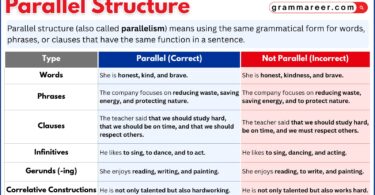
As we learned, modal verbs make your sentences more meaningful. They let you talk about ability, permission, possibility, necessity, and obligation, and are often used in questions and negatives. They’re easy to use because they don’t change with tense or subject, making them simple but powerful for clear communication.
You May Also Like