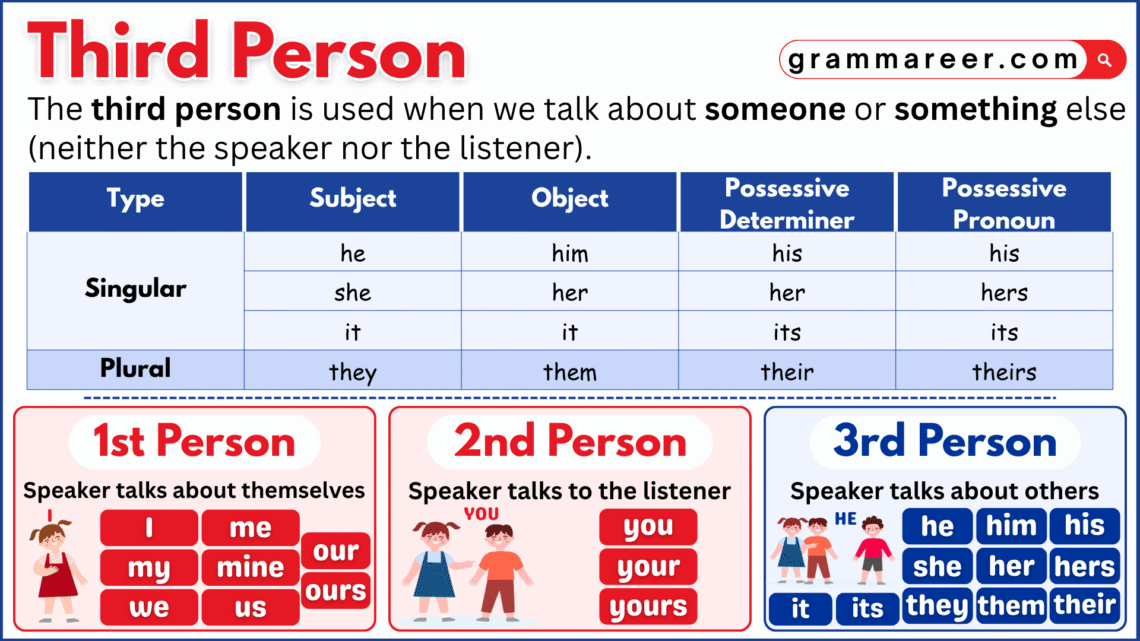
Have you ever talked about someone else and used words like he, she, or they? That’s what we call the third person in English. It’s when we talk about people instead of to them. For example, when you say She loves ice cream or They are studying for the test, you’re using the third person. It’s a common point of view in storytelling, writing, and everyday conversation because it helps describe others clearly and naturally.
In this article, we’ll learn what the third person means, how it’s used, and see some easy examples to understand it better.
Table of Contents
What is a Third Person?
Third person is a way of speaking or writing where we talk about someone rather than to them. Instead of saying I or you, we use names or pronouns like he, she, it, or they. For example, when you say Sara loves painting or They are playing outside, you’re using the third person. It’s a common point of view in stories, essays, and everyday speech because it helps describe what others are doing or feeling without directly involving yourself or the listener.
For Example:
- He plays football every evening.
- She loves reading mystery books.
- It looks like it’s going to rain.
- They are planning a trip to the mountains.
- The teacher said he will check the papers tomorrow.
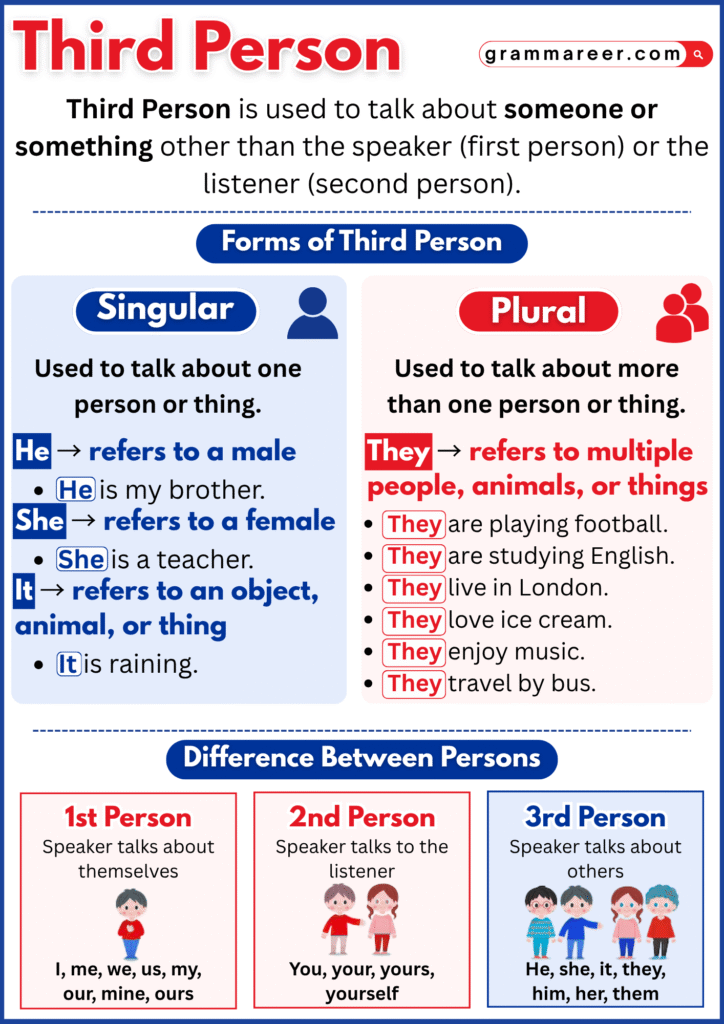
Third-person pronouns:
Third-person pronouns are the words we use when talking about someone or something else—not ourselves and not the person we’re speaking to. Words like he, she, it, and they are all third-person pronouns. They help us talk about people, animals, things, or even ideas.
Just like other pronouns, third-person pronouns can be singular or plural, and they come in a few different forms: subject, object, possessive, and reflexive.
| Type | Singular | Plural |
|---|---|---|
| Subject | he, she, it | they |
| Object | him, her, it | them |
| Possessive | his, hers, its | theirs |
| Reflexive | himself, herself, itself | themselves |
The word they is a bit special—it can be used for one person when we don’t know their gender (like Someone left their bag here), or for many people when we’re talking about a group (like They are my friends).
Third-Person Subject Pronouns (He, She, It, They)
Third-person subject pronouns are words like he, she, it, and they that tell us who or what is doing the action in a sentence. They usually come before the verb and show the main focus of the sentence.
For example:
- He works at the library.
- She loves playing the guitar.
- It looks like it’s going to rain.
- They enjoy watching movies together.
The word it is used for things, animals, or ideas—not for people. And they can be used for more than one person or thing (plural), or even for one person when we don’t know their gender.
Sometimes, these pronouns appear after a linking verb to rename or describe the subject.
Example:
- The winner of the race was he.
You can also use them in compound subjects, but remember to use subject pronouns, not object pronouns.
Examples:
- ❌ Me and her are going shopping today.
- ✅ She and I are going shopping today.
Third-Person Object Pronouns (him, her, it, them)
We use object pronouns when the person or thing is receiving an action, not doing it. In the third person, these pronouns are him, her, it, and them.
Think of it this way — if someone does something to another person or thing, the receiver of that action takes an object pronoun.
When Do We Use Third-Person Object Pronouns?
Here are the main times you’ll need them:
- After prepositions – like to, with, for, beside, or about.
- As a direct object – when someone receives the action of a verb.
- As an indirect object – when someone benefits from or is affected by the action.
Examples:
| Use | Example |
|---|---|
| Direct object | • The teacher called him to the front of the class. |
| Indirect object | • I sent her a birthday card yesterday. |
| Object of a preposition | • The kids played with them in the park. |
Using “It” as an Object Pronoun:
The word it is a little different — it’s used for things, animals, ideas, or situations (but not people). You can use it both as a subject or an object pronoun.
| Use | Example |
|---|---|
| Subject pronoun | • It looks like it’s going to rain soon. |
| Object pronoun | • She picked up the book and placed it on the shelf. |
Third-Person Possessive Pronouns (his, hers, its, theirs)
We use possessive pronouns to show that something belongs to someone or something else. In the third person, these pronouns are his, hers, its, and theirs. They help us talk about ownership without repeating names or nouns.
These pronouns replace the noun instead of sitting before it. That’s what makes them different from possessive determiners like his, her, its, or their, which always come before a noun (e.g., her bag, their car).
- Possessive pronoun: stands alone → The red dress is hers
- Possessive determiner: before a noun → her dress
Examples:
- That blue car is his, not mine.
- The garden with the white roses is theirs.
- The small puppy wagged its tail happily.
Third-Person Reflexive Pronouns (himself, herself, itself, themselves, themself)
Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject and the object of a sentence are the same person or thing. In the third person, we use himself, herself, itself, themselves, and sometimes themself (for one person whose gender isn’t known or specified).
Think of reflexive pronouns as a way to show that someone is doing something to or for themselves.
Examples:
- The dog hurt itself while jumping off the sofa.
- They prepared themselves for the final exam.
- John pushed himself to finish the marathon.
When We Use the Third Person
We use the third person when we want to talk about someone or something instead of ourselves. It’s perfect for storytelling, academic writing, or any situation where you need to sound clear, objective, or formal.
In Stories and Fiction Writing:
Writers often use the third person to tell stories from an outside view. It helps readers see what each character is doing or feeling without the writer being part of the story.
For Examples:
- He ran as fast as he could to catch the train.
- She dreamed of visiting Paris one day.
- They built a small house near the lake.
In Academic and Formal Writing:
In essays, reports, and research papers, the third person keeps the tone professional and unbiased. It focuses on facts rather than personal opinions.
For Examples:
- The study suggests that regular reading improves vocabulary.
- Students should complete all assignments before the deadline.
- The research highlights the importance of clean energy.
In Business and Professional Writing:
Businesses use the third person to sound polite, confident, and professional when communicating with clients or the public.
For Examples:
- The company offers a full refund within 30 days.
- ABC Store provides high-quality products at affordable prices.
- The management team is working on improving customer service.
In Everyday Conversation or News Reporting:
The third person helps describe what others do or say in daily life or journalism, keeping the focus on them rather than the speaker.
For Example:
- Ali is studying hard for his exams.
- They announced the results yesterday.
- The president addressed the nation last night.
Using the third person makes your writing sound more formal, balanced, and descriptive—ideal for stories, reports, and clear communication.
First, Second, and Third Person Pronouns
In English, pronouns change depending on who is speaking and who they’re talking about. We usually divide them into first person, second person, and third person. Let’s break them down in a simple way.
| Person | Subject Pronouns | Object Pronouns | Possessive Determiners (before a noun) | Possessive Pronouns (stand alone) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| First Person Singular | I | me | my | mine |
| First Person Plural | we | us | our | ours |
| Second Person Singular & Plural | you | you | your | yours |
| Third Person Singular | he, she, it | him, her, it | his, her, its | his, hers, its |
| Third Person Plural | they | them | their | theirs |

Examples of Third Person:
- He wakes up early every morning.
- She enjoys listening to soft music.
- It looks like it’s going to rain.
- They love going on road trips.
- Ali works at a software company.
- Sara writes beautiful poems.
- The teacher explains the lesson clearly.
- The dog barks loudly at strangers.
- The sun rises in the east.
- The children are playing in the garden.

FAQs about Third Person Pronouns
Third person pronouns are words we use to talk about people or things other than ourselves or the person we’re speaking to. They include words like he, she, it, they, him, her, and them.
You use third person pronouns when referring to someone or something that isn’t part of the conversation. For example, instead of saying I like tea or you like tea, you’d say she likes tea or they like tea.
Here are some examples showing how third person pronouns are used:
• He loves playing football.
• She is reading a new novel.
• It looks really cute.
• They are traveling to London.
• The teacher called him to the office.
• Everyone admired her performance.
• The cat cleaned itself after eating.
• The children made themselves sandwiches.
You May Also Like