Adjectives and types of adjectives are really important words that we use a lot. They make our language more interesting and help us explain things better. Adjectives are words that describe nouns or pronouns, like telling us what something looks like or how it feels. If we didn’t have adjectives, our words would be a bit boring and not so clear. So, let’s learn about adjectives, what they are, the different types of adjectives, and see some examples. Ready? Let’s go!
Table of Contents
What is Adjective?
In simple terms, an adjective is a word that describes or gives more information about a noun. Nouns are the names of people, places, things, or ideas, and adjectives step in to tell us more about them.
Examples:
- The happy children played in the park.
- She wore a colorful dress to the party.
- Our cat is playful and loves chasing
- The tall trees provided shade on a sunny day.
- I found a delicious recipe and cooked a tasty meal.
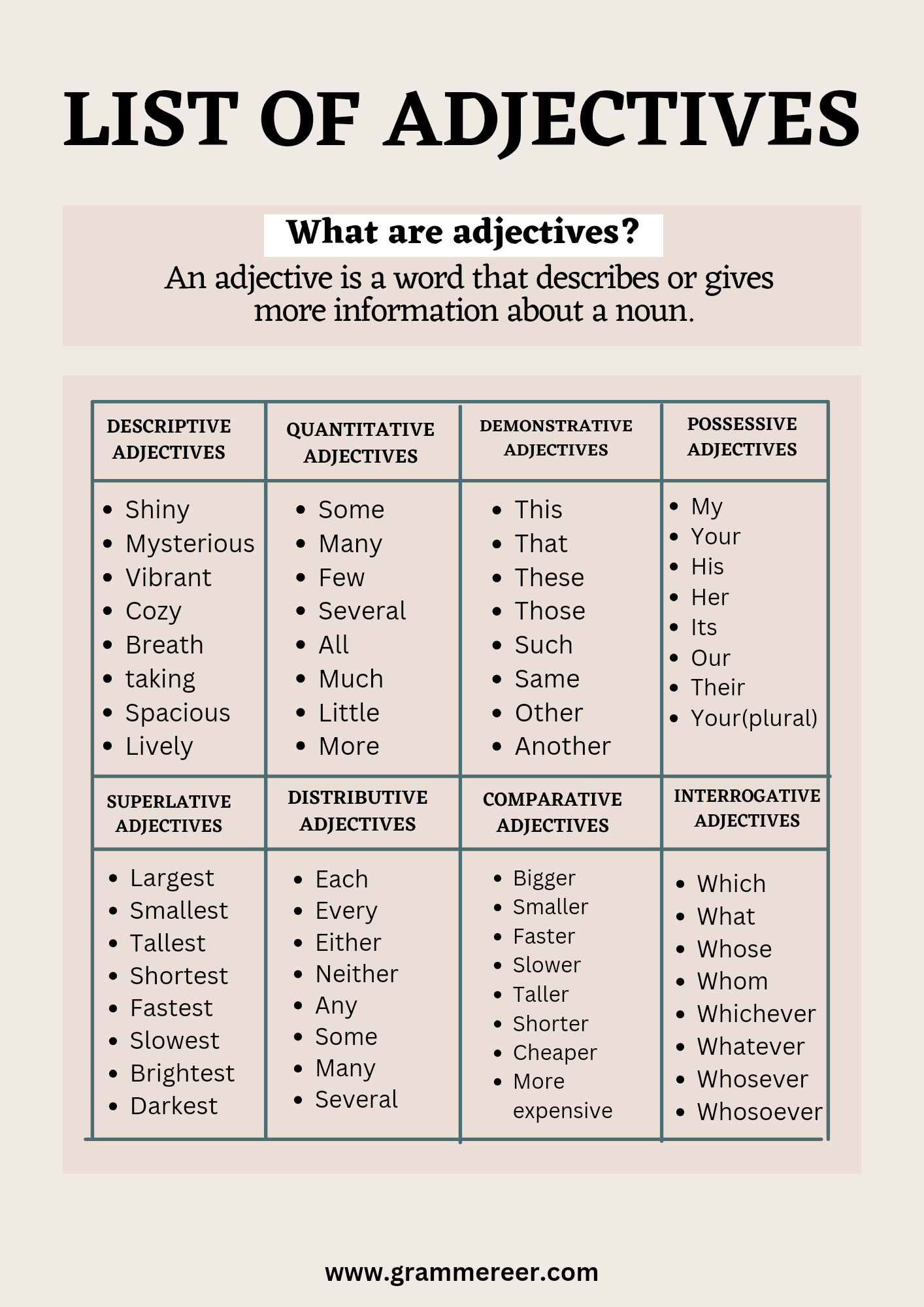
List of Common Adjectives with Types
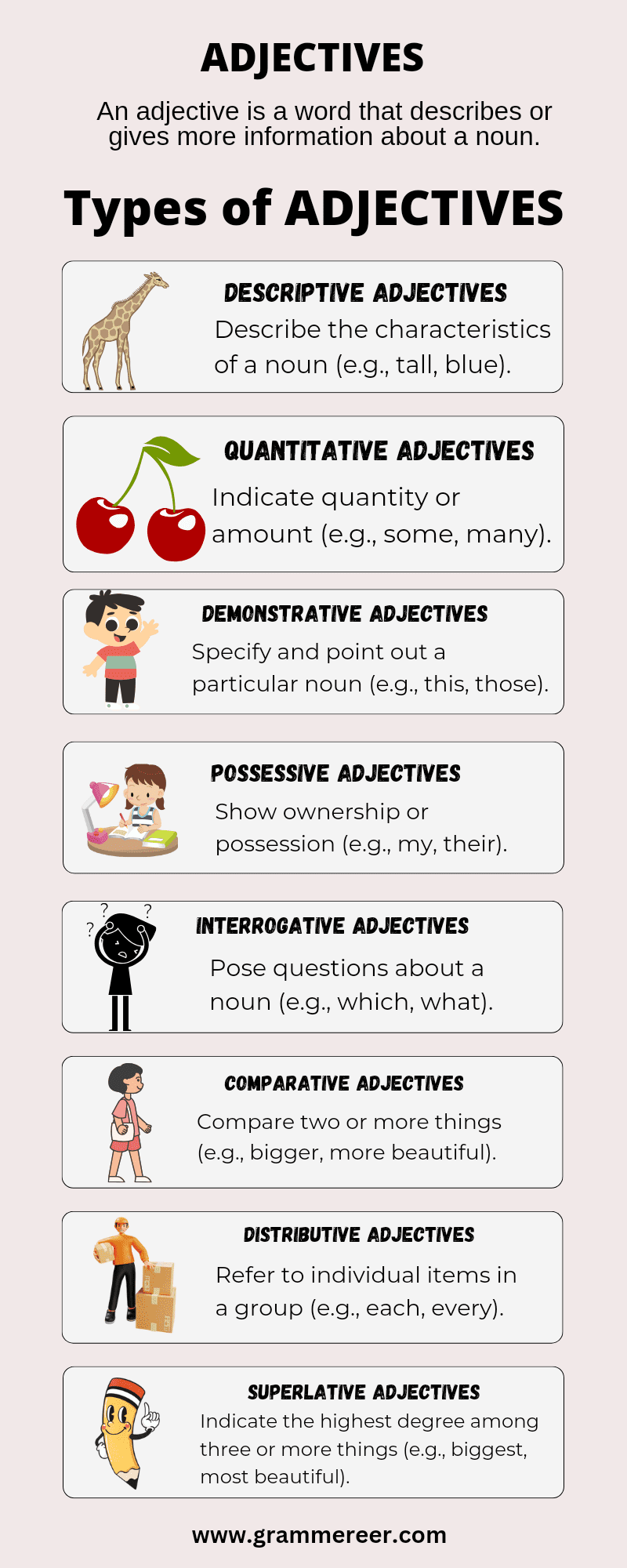
Types of Adjectives
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives are words that tell us more about a noun by describing its qualities or characteristics. They add details that help create a clearer picture in our minds. Whether it’s a color, size, or emotion, descriptive adjectives make nouns more interesting and help us understand them better. (e.g., Bright Sun: The word “bright” describes the sun, telling us about its intensity and shining quality.)
Examples:
- The red apple gleamed on the tree.
- She wore a soft scarf to stay warm.
- The gigantic elephant trumpeted loudly.
- The playful puppy chased its tail.
- We admired the beautiful
Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives are words that help us express the amount, quantity, or number of something. These adjectives give us information about how much or how many of a particular noun there is. In simple terms, they are like the counting words that tell us more about the quantity involved. (e.g., Many books are on the shelf. “Many” gives us an idea that there is a large number of books.)
Examples:
- Three kittens were playing in the backyard.
- I need two cups of flour for the recipe.
- The library has many books on various subjects.
- We planted five sunflowers in the garden.
- She received several awards for her academic achievements.
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives are words that help us specify or point out a particular noun. They indicate whether the noun is near or far, making our communication more precise. (e.g., Can you see those mountains? (Points out mountains at a distance.)
Examples:
- I like this
- Can you pass me those keys?
- These cookies taste delicious.
- Look at that beautiful sunset.
- I need such help sometimes.
Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives are words that show ownership or possession. They help us understand who something belongs to. (e.g., This is my book. (The book belongs to me.)
Examples:
- This is my favorite sweater.
- Did you find your keys?
- I borrowed his laptop for the presentation.
- Her cat is adorable and playful.
- Let’s plan for dinner at our place tonight.
Interrogative Adjectives
Interrogative adjectives are words that help us ask questions about nouns, aiming to gather more information. Interrogative adjectives, such as “which,” “what,” and “whose,” assist in shaping questions to particular aspects or characteristics of the nouns we’re discussing. (e.g., What book are you reading? (Seeks information about a particular book.)
Examples:
- Which book do you want to read?
- What color is your car?
- Whose keys are on the table?
- Whom did you invite to the party?
- Which team won the championship?
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are words that help us compare two or more things, highlighting the differences in their qualities. Comparative adjectives show the difference in degree or quality between two nouns. (e.g., Faster Car: The sports car is faster than the regular car.)
Examples:
- The cheetah is faster than the tortoise.
- My sister’s phone is smaller than mine.
- The sun is brighter than the moon.
- Sarah feels happier today than yesterday.
- Ali is taller than his younger brother.
Distributive Adjectives
Distributive adjectives highlight individual items within a group, telling us more about each one separately. They help us understand how things are shared or distributed. (e.g., Every student received a certificate. “Every” points to each student individually, showing that all of them received a certificate.)
Examples:
- Each student received a gold star for their hard work.
- Every house on the street has a unique design.
- You can choose either movie for our movie night.
- Neither parent knew about the surprise birthday party.
- Any book from the library is available for you to borrow.
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative adjectives express the highest level of a particular quality among a group of three or more items. (e.g., Mount Everest is the* tallest* mountain in the world. “Tallest” informs us that, compared to all other mountains, Mount Everest stands the highest.)
Examples:
- Mount Everest is the largest mountain in the world.
- The ancient ruins are the oldest structures in the city.
- The central market is the busiest place in the town.
- The giraffe is the tallest animal in the zoo.
- Late at night, the neighborhood is the quietest it has ever been.
Types of Adjectives Examples
- The blue ocean stretched endlessly before us.
- He bought a new car yesterday.
- We enjoyed a delicious meal at the restaurant.
- The tiny kitten played with a ball of yarn.
- She received a surprising gift on her birthday.
- This is the last piece of cake in the kitchen.
- The sunny day lifted everyone’s spirits.
- He lives in a beautiful house by the lake.
- The hardworking students excelled in their exams.
- We explored the ancient ruins of the city.
- The movie had a thrilling plot that kept us on the edge of our seats.
- She wore a elegant dress to the party.
- I prefer the quiet moments of solitude.
- The red roses in the garden bloomed beautifully.
- My grandmother’s stories are always captivating.
- They found a lost puppy wandering on the street.
- The fast train took us to the city in no time.
- The hilarious comedian had the audience in stitches.
- We visited a historic museum to learn about the past.
- The patient teacher explained the concept until everyone understood.
You May Also Like