Verb tenses in English are one of the most essential grammar topics to master if you want to speak and write confidently. They help us express not just actions, but also when those actions happen—whether in the past, present, or future. Without tenses, our communication would lose clarity and meaning.
In this article, we’ll explore the 12 types of verb tenses, their rules, and plenty of easy examples. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how verb tenses work and how to use them naturally in your everyday conversations and academic writing.
Table of Contents
What Are Verb Tenses?
Verb tenses tell us when an action happens—in the past, the present, or the future.
For example:
- Past: I walked to school.
- Present: I walk to school.
- Future: I will walk to school.
But verb tenses don’t just show time. They also tell us whether an action is ongoing, finished, or happens regularly. This extra detail is called the aspect of the verb.
In English, verbs often change their form to show tense (walk → walked), or sometimes use a helping verb like will or have. This makes it clear for the reader or listener to understand when something took place and how it happened.
Definition of Verb Tenses
A verb tense is a form of a verb that shows the time of an action or event. In simple words, verb tenses tell us when something happens—whether it’s in the past, happening right now, or will happen in the future.
Example:
- She studies every day. (Present)
- She studied yesterday. (Past)
- She will study tomorrow. (Future)
In English, verb tenses also show whether an action is complete, ongoing, or repeated, which makes our sentences more meaningful and precise.
How Do You Identify a Verb in English?
Before we start learning about verb tenses, it’s important to first understand what a verb is and how to spot it in a sentence.
A verb is usually described as a word that shows action or a state of being. For example: run, jump, sing (action words) or am, is, was (states of being). Sounds simple, right? But sometimes, verbs are trickier to identify.
Example:
- The cat sleeps on the sofa every afternoon.
At first glance, you might think cat or sofa are important, but the verb here is sleeps — because it shows what’s happening and when.
How many verb tenses are in English?
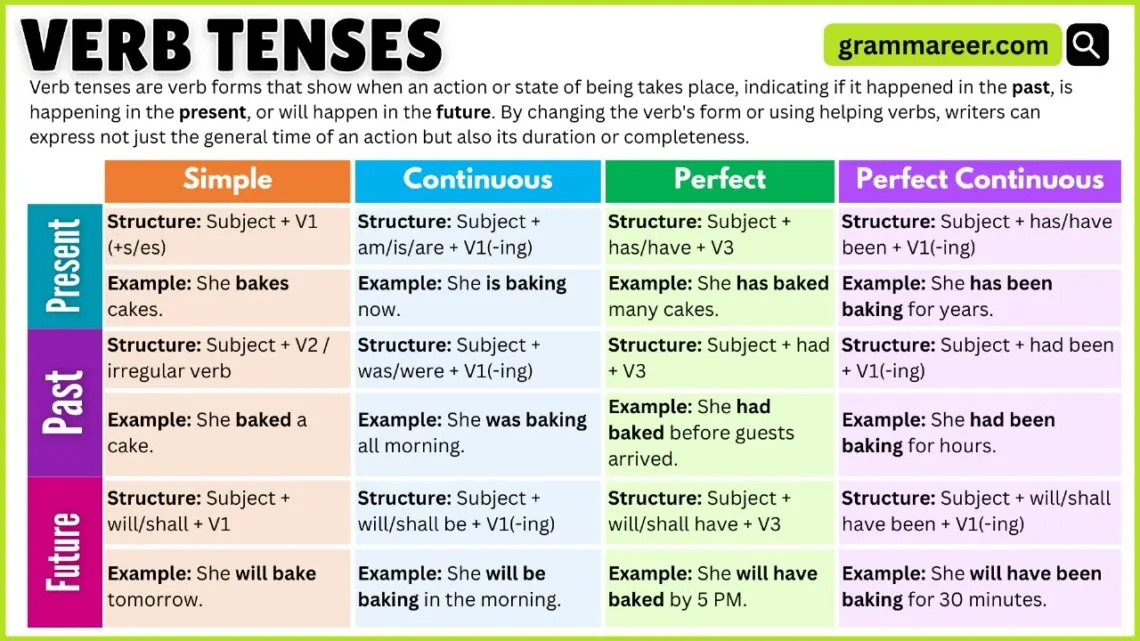
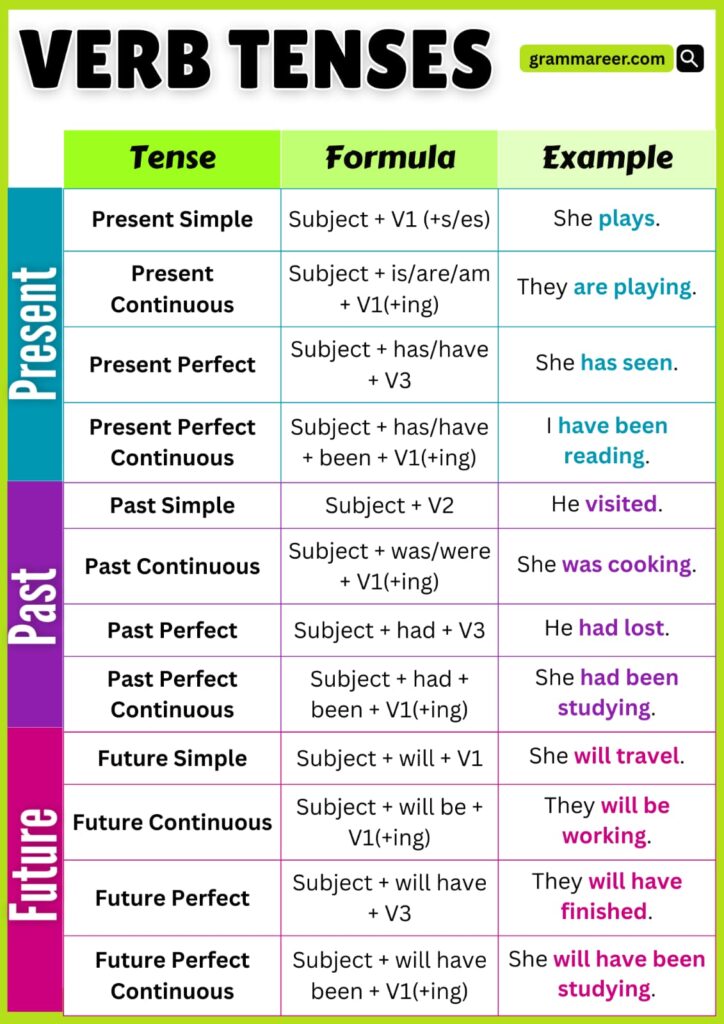
In English, there are 12 verb tenses. These tenses help us express not only the time of an action (past, present, or future) but also its state (whether it’s ongoing, completed, or repeated).
Think of it this way: the three main tenses (past, present, future) each have four different forms. Together, they make up the 12 verb tenses in English.
List of Verb Tenses
The list of verb tenses in English shows how a single verb can change its form to express time and aspect, making it easier to understand when and how an action happens.
Infinitive: to write
| Tense | Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous |
| Past | wrote | was writing | had written | had been writing |
| Present | write / writes | am / is / are writing | have / has written | have / has been writing |
| Future | will write | will be writing | will have written | will have been writing |
Past, Present, and Future Tenses
n English, all verb tenses are built around three main divisions of time: past, present, and future.
- The present tense shows actions happening right now.
- The past tense shows actions that already happened.
- The future tense describes actions that will happen later.
These three time frames are the foundation, and from them, we create the 12 verb tenses in English.
Simple Tense
The simple tense is the most basic form of verb tenses. It simply tells us if something happens in the past, present, or future—without adding extra details.
For example:
- I walk to school every day. (Present Simple)
- I walked to school yesterday. (Past Simple)
- I will walk to school tomorrow. (Future Simple)
Because it’s straightforward and has the fewest rules, the simple tense is the easiest to learn.
Perfect Tense
The perfect tense is a little more advanced. It shows actions that are completed or connected to another point in time.
For example:
- I have played soccer since I was a child. (The action started in the past and continues now.)
- I played soccer when I was a child. (The action happened only in the past and is not connected to the present.)
Perfect tenses are formed by using have/has/had + the past participle of the main verb.
Continuous Tense
The continuous tense (also called the progressive tense) is used for actions that are ongoing or take time before finishing.
For example:
- They are studying all night.
- (The action is still happening and continues for hours.)
Note: Continuous tenses are usually not used with stative verbs like want, love, have, or need.
Continuous tenses are formed with a version of be + the verb’s -ing form.
Perfect Continuous Tense
The perfect continuous tense combines both perfect and continuous aspects. It describes actions that are ongoing and connected to a specific time.
For example:
- I have been studying English for three years.
- (The action started in the past and is still happening now.)
This tense is formed using have/has/had + been + the verb’s -ing form.
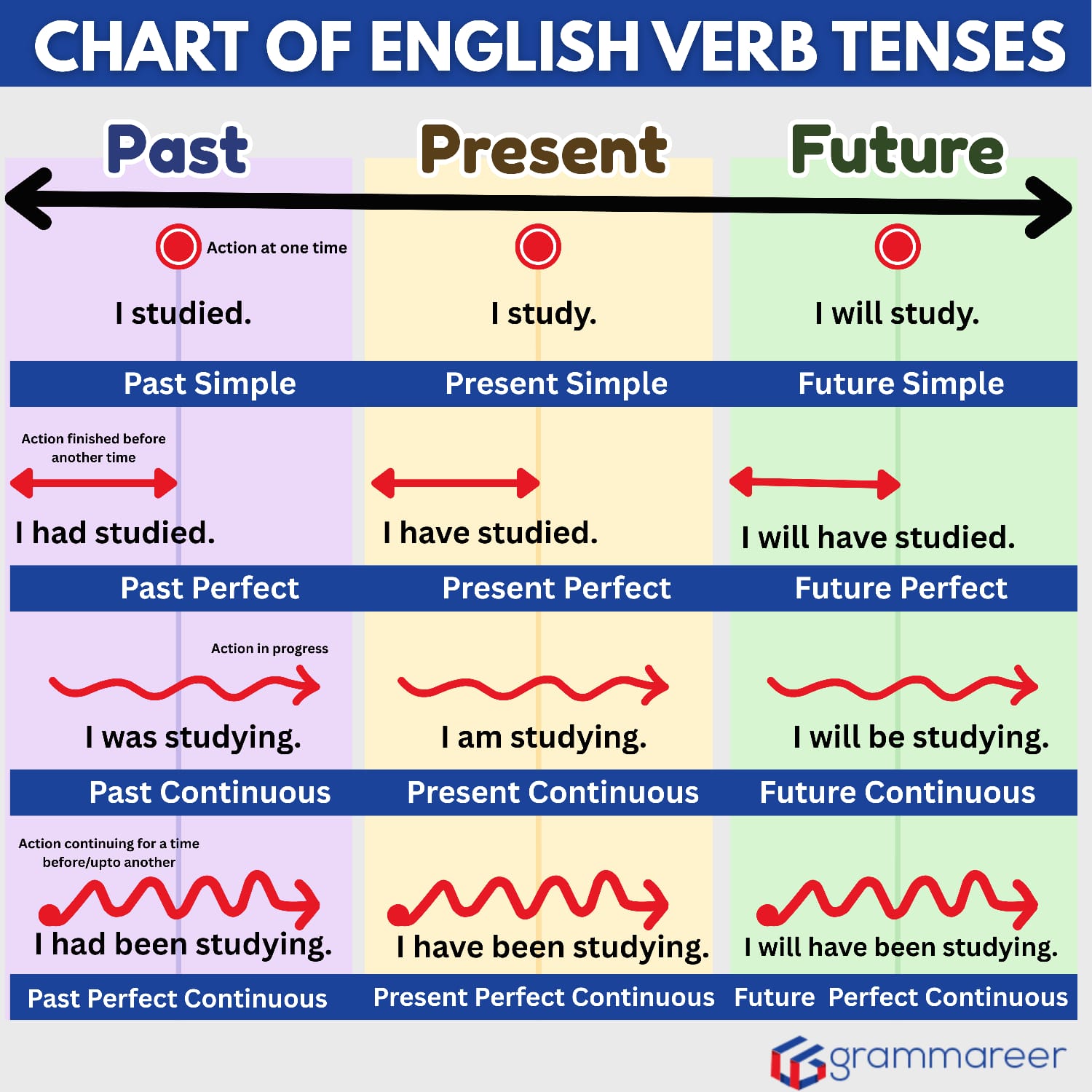
Verb Tenses Chart
A verb tenses chart is a quick reference that shows how verbs change in the past, present, and future across simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous forms.
Present Tenses
Present tenses in English help you talk about actions happening right now, habits you do regularly, and experiences that are still connected to the present moment. There are four present tenses, and each one shows a different relationship between time and action.
| Present Tense | Description | Form | Example |
| Simple Present | Used to describe facts, habits, and general truths. | Subject + base verb (+ s/es for third person) | She writes every day. |
| Present Continuous | Used for actions happening right now or around the current time. | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing | She is writing right now. |
| Present Perfect | Used for actions that happened in the past but are still connected to the present. | Subject + have/has + past participle | She has written three pages today. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | Used for actions that started in the past and are still continuing, often showing duration. | Subject + have/has been + verb-ing | She has been writing since morning. |
Past Tenses
Past tenses in English are used to talk about actions, events, or situations that happened before now. They help us show whether something was completed, ongoing, or happened before another event in the past. There are four types of past tenses, and each one gives a slightly different meaning.
| Past Tense | Description | Form | Example |
| Simple Past | Describes completed actions at a specific time in the past. | Subject + past tense verb | She wrote a letter yesterday. |
| Past Continuous (Progressive) | Describes actions that were ongoing at a certain moment in the past. | Subject + was/were + verb-ing | She was writing a letter when he called. |
| Past Perfect | Describes actions completed before another past event. | Subject + had + past participle | She had written a letter before she left home. |
| Past Perfect Continuous | Describes ongoing actions that continued up until another moment in the past. | Subject + had been + verb-ing | She had been writing a letter for an hour before dinner. |
Future Tenses
Future tenses in English are used to describe actions and situations that haven’t happened yet but will occur later. They help us talk about predictions, ongoing future activities, or actions that will be finished by a certain time. There are four main future tenses, and each shows a different aspect of time.
| Future Tense | Description | Form | Example |
| Simple Future | Used to express actions or events that will happen later. | Subject + will + base verb | She will write a story tomorrow. |
| Future Continuous (Progressive) | Shows actions that will be ongoing at a particular time in the future. | Subject + will be + verb-ing | She will be writing a story when you visit. |
| Future Perfect | Describes actions that will be completed before a certain point in the future. | Subject + will have + past participle | She will have written three stories by next week. |
| Future Perfect Continuous | Describes actions that will continue up until another moment in the future, often emphasizing duration. | Subject + will have been + verb-ing | She will have been writing a story for two hours by the time dinner is ready. |
How Important Is It to Know About Tenses?
Tenses are the backbone of English grammar. Imagine trying to talk without tenses—everything would sound confusing and incomplete.
Knowing tenses is important because:
- They tell us when an action happens – past, present, or future.
- They bring clarity to your message, so people understand exactly what you mean.
- They help you build complex sentences, making your communication stronger and more effective.
In short, without tenses, English communication becomes unclear and messy. That’s why it’s essential to learn all twelve tenses and understand how to use them in real life.
If you want to speak and write English fluently, mastering tenses isn’t optional—it’s a must.
FAQS
In English grammar, a tense shows the time of action. It tells us whether something happens in the past, is happening now, or will happen in the future. Without tenses, sentences lose their meaning and become unclear.
English grammar has 12 tenses, divided into past, present, and future. Here’s the list:
• Simple Present Tense
• Present Continuous Tense
• Present Perfect Tense
• Present Perfect Continuous Tense
• Simple Past Tense
• Past Continuous Tense
• Past Perfect Tense
• Past Perfect Continuous Tense
• Simple Future Tense
• Future Continuous Tense
• Future Perfect Tense
• Future Perfect Continuous Tense
These tenses help us clearly express when and how actions happen.
Tenses are important because they give meaning to sentences. Without them, you wouldn’t know when an action happens. For example:
• I eat (present) – happening now.
• I ate (past) – already happened.
• I will eat (future) – going to happen.
By using the correct tense, you make your sentences clear, accurate, and easy to understand.
You May Also Like
Active and Passive Voice
Parts of Speech
Demonstrative Adjectives